
GLP-1 weight loss drugs are a hot topic. Social media and long clinic waits make it hard to know what’s true. This section will clear up the myths and facts about these drugs.
GLP-1 drugs, like semaglutide and tirzepatide, were first for type 2 diabetes. Now, they’re studied for weight loss too. Studies show they help with weight and blood sugar. They also improve heart health in high-risk people.
It’s important to know the difference between Ozempic and Wegovy. Ozempic is for diabetes, while Wegovy is for weight loss. Tirzepatide, used in Zepbound, is for obesity. Knowing these facts helps make informed choices with your doctor.
Results depend on the dose, how long you take it, and your lifestyle. Side effects like nausea and cost are common. But, for many, GLP-1 drugs offer a chance for better health with the right lifestyle changes.
Key Takeaways
- GLP-1 myths fade when you compare headlines with high-quality trials and cardiometabolic health outcomes.
- Ozempic facts differ from Wegovy science; same ingredient, different indications and doses.
- Tirzepatide facts show strong weight loss in obesity alongside glucose benefits.
- Semaglutide evidence includes meaningful weight loss and reduced major cardiac events in certain groups.
- Obesity drugs evidence supports long-term treatment plus nutrition, activity, and sleep.
- Side effects and cost exist; the truth about weight loss drugs includes pros and cons.
- Work with a clinician to tailor dose, track progress, and manage risks for durable results.
Why GLP-1s Are Everywhere Right Now
Turn on the TV or open your feed and you’ll see it: a wave of interest in GLP-1 medicines. This interest is fueled by visibility—before-and-after photos, red-carpet chatter, and debates about celebrity weight loss drugs. But the pull goes deeper, tied to health, access, and cost.
Stories about rapid results meet real concerns about the obesity epidemic United States, where more people are seeking safe, supervised care. This mix has pushed conversation, clinics, and supply chains into the spotlight.
From celebrity buzz to a 400% prescription surge (2019–2023)
High-profile mentions drove curiosity, and so did memes about “Ozempic face.” As Ozempic popularity grew, so did off-label chatter and knockoffs. Pharmacies reported backorders, reflecting broad prescription growth GLP-1 for both diabetes and weight care.
People cite weekly dosing, less “food noise,” and visible changes. This momentum, plus Wegovy demand and a Zepbound surge, keeps attention high across clinics and social media.
A market projected to exceed $100B by 2030
Analysts see a multi-year boom fueled by new indications, bigger trials, and manufacturing scale-up. Premium prices and repeat fills add to the outlook, as employers and insurers weigh coverage and adherence.
Rising Wegovy demand, ongoing Ozempic popularity, and the Zepbound surge shape expectations. Pipeline competitors and combo therapies could expand choices and push innovation.
Rising obesity and type 2 diabetes in the U.S. driving demand
The obesity epidemic United States now touches tens of millions, with type 2 diabetes rising alongside. Patients want options that fit daily life and reduce risks, not just weight.
Trials show double-digit weight loss with semaglutide and tirzepatide. Those outcomes, plus fewer swings in blood sugar, help explain steady prescription growth GLP-1 in primary care and specialty practices.
Why a cardiologist’s perspective matters for weight and heart health
Excess weight, insulin resistance, and high blood pressure often travel together. GLP-1s are part of a broader plan to target them at once, linking weight control with heart outcomes.
Evidence points to cardiovascular risk reduction in select patients, including fewer major events and better heart failure symptoms. That’s why cardiology now joins endocrinology and primary care in treatment decisions.
| Driver | What’s Changing | Impact on Patients | Brands in Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Buzz | Celebrity weight loss drugs trend across TV and social platforms | Higher awareness, faster inquiries, faster first visits | Ozempic popularity, Wegovy demand |
| Clinical Results | Meaningful weight loss and cardiovascular risk reduction in trials | Motivation to start and stay on therapy | Wegovy, Zepbound surge |
| Access & Coverage | Prior authorization and variable benefits affect starts | Delays, shortages, and switching between options | Ozempic, Wegovy, Zepbound |
| Epidemiology | Obesity epidemic United States and rising type 2 diabetes | Broader prescription growth GLP-1 across specialties | Semaglutide, Tirzepatide |
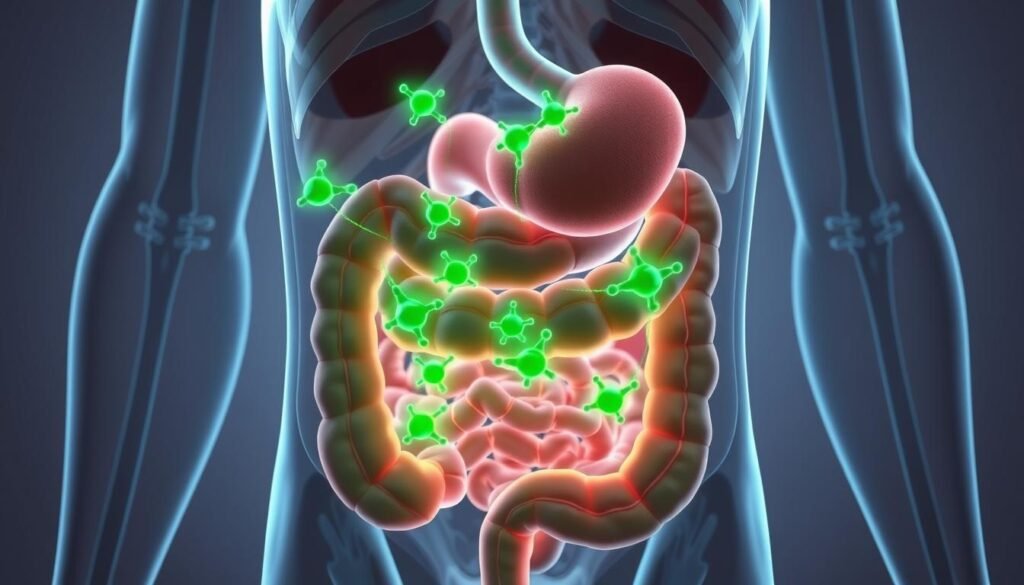
How GLP-1s Work in the Body
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic a natural hormone that increases after eating. This hormone helps match hunger signals with blood sugar levels. It also helps use energy more steadily. Drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide keep these signals active for a week, influencing daily choices and metabolism.
Brain pathways: appetite, cravings, and fullness cues
In the brain, these medicines reduce “food noise” and enhance fullness signals. This helps control appetite by reducing the urge to snack and increasing satisfaction after eating normal amounts. Understanding how semaglutide works in these brain areas helps explain why people eat more steadily and have fewer cravings.
Tirzepatide, a dual agonist, works even better by combining GLP-1 with GIP signaling. This makes people feel fuller and less tempted by high-calorie foods, shaping their eating habits over time.
Gut effects: slower gastric emptying and common GI side effects
In the gut, these drugs slow down how fast food leaves the stomach. This leads to feeling full sooner and eating smaller meals. But, it can also cause nausea, diarrhea, or constipation, which often gets better as the body adjusts.
These gut effects are a direct result of the GLP-1 mechanism. They also explain why eating slowly and stopping when feeling full is helpful.
Metabolic actions: insulin secretion, blood sugar control, and vascular impact
After meals, GLP-1–based drugs help release insulin in a way that depends on glucose levels. This helps control blood sugar spikes and improve A1C levels without increasing the risk of low blood sugar. Better blood sugar control also helps stabilize hunger swings caused by rapid changes in blood sugar.
These drugs also lower blood pressure and improve lipid levels, showing broader benefits for the heart and blood vessels. These changes, along with weight loss, contribute to better heart health in daily life.
Beyond weight: links to heart, kidney, and sleep apnea outcomes
Research is exploring how these drugs affect more than just weight. Studies show fewer major heart events in some groups and better symptoms in heart failure. This suggests these drugs have both metabolic and vascular benefits.
Kidney markers often improve along with better blood sugar control, and losing weight may help with sleep apnea. These findings show how semaglutide and tirzepatide work together to improve health across different organs through better appetite control, insulin support, and lasting benefits for the heart and blood vessels.
GLP-1 myths, GLP-1 weight loss facts, truth about weight loss drugs, Ozempic
Social feeds are full of GLP-1 myths and obesity drug misconceptions. Let’s focus on GLP-1 weight loss facts and clear things up. We’ll also compare Wegovy and Ozempic and share semaglutide facts. Plus, we’ll debunk tirzepatide myths.

Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new drugs
This idea skips the history. GLP-1–based therapies have been in diabetes care for years. They have a long history that contradicts many obesity drug misconceptions.
Modern versions have longer half-lives and weekly dosing. This makes them easier to use, which is why GLP-1 weight loss facts look strong in trials.
Semaglutide facts show a roughly seven-day half-life, while tirzepatide runs about five days. These details matter when weighing data and filtering out tirzepatide myths that spread online.
Fact: FDA-approved for type 2 diabetes for 15+ years; newer dosing improved adherence
Long clinical use helps separate noise from evidence. Weekly pens and step-wise titration increased persistence and supported better outcomes. That evolution explains why Wegovy vs Ozempic debates often hinge on dose, schedule, and the real-world Ozempic truth.
When you look beyond headlines, the semaglutide facts and broader GLP-1 weight loss facts reflect rigorous studies, not hype.
Myth: Ozempic is FDA-approved for weight loss
Here’s where the Ozempic truth matters. Ozempic is authorized for type 2 diabetes, which is why some GLP-1 myths keep circling. Confusion fuels obesity drug misconceptions and blurs the line between brands and indications.
Wegovy vs Ozempic is not a branding quirk; it is a regulatory and dosing distinction tied to outcomes and patient selection.
Fact: Ozempic is for diabetes; Wegovy (same semaglutide) is approved for obesity
Wegovy contains semaglutide at higher doses for chronic weight management, while Ozempic uses the same active ingredient for glycemic control. Those semaglutide facts are key to patient counseling and cut through tirzepatide myths by showing how indications guide use.
Understanding these labels supports informed care and keeps GLP-1 weight loss facts front and center.
| Brand | Active ingredient | FDA indication | Dosing cadence | Key takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozempic | Semaglutide | Type 2 diabetes | Weekly injection | Core to the Ozempic truth: for glycemic control, not weight loss labeling |
| Wegovy | Semaglutide | Chronic weight management | Weekly injection | Wegovy vs Ozempic differs by approved use and dose, despite shared molecule |
| Mounjaro | Tirzepatide | Type 2 diabetes | Weekly injection | Helps clarify tirzepatide myths by separating diabetes and obesity labels |
| Zepbound | Tirzepatide | Chronic weight management | Weekly injection | Counters obesity drug misconceptions with clear indication for weight |
Which Drug, Which Name? Understanding Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound
Brand names tell us how to use a drug, its dose, and how to take it. Knowing the difference between Ozempic and Wegovy, and Mounjaro and Zepbound helps us understand what to expect. This includes the results, how to get the drug, and the steps doctors follow to manage side effects.
Semaglutide: Ozempic (diabetes) vs. Wegovy (obesity) and dose differences
Both Ozempic and Wegovy use weekly injections. But, they have different doses for different goals. Ozempic helps with type 2 diabetes and uses lower doses. Wegovy is for weight loss and uses higher doses, showing better results in long-term trials.
Patients often wonder about switching between Ozempic and Wegovy. The labels, pen colors, and doses are different. So, pharmacies can’t swap them without a new prescription.
Tirzepatide: Mounjaro (diabetes) vs. Zepbound (obesity) and similar pens/doses
Mounjaro and Zepbound share the same molecule and use the same weekly pen. They differ in their use for diabetes versus obesity. The steps to increase the dose are slightly different for each.
The dose of tirzepatide starts low and increases over weeks. This helps patients get used to it. Some plans may cover one more than the other, affecting costs and which pen is chosen.
Liraglutide: Victoza vs. Saxenda and earlier-generation efficacy
Liraglutide is taken daily. Saxenda and Victoza are the same drug but for different reasons. Saxenda is for obesity, and Victoza is for diabetes. Saxenda Victoza has less weight loss than newer drugs but is easier to take daily.
Insurance coverage for Saxenda Victoza might be different. This means pharmacies might need to get approval before giving it out.
Oral vs. injectable options and why titration timelines matter
Rybelsus is a pill for diabetes, unlike most obesity treatments which are injections. It needs to be taken in the morning and on an empty stomach for best absorption.
The way doctors increase doses helps avoid side effects like nausea and diarrhea. Slow increases help patients stick with treatment, even when results slow down or when they need to switch supplies.
| Drug/Brand | Indication | Route | Dosing Pattern | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozempic (semaglutide) | Type 2 diabetes | Injection, weekly | Lower maintenance; staged increases | Not approved for obesity; compare Ozempic vs Wegovy before switching |
| Wegovy (semaglutide) | Chronic weight management | Injection, weekly | Higher target dose via gradual uptitration | Trial-verified weight loss; semaglutide dosing differs from Ozempic |
| Mounjaro (tirzepatide) | Type 2 diabetes | Injection, weekly | Tirzepatide dosing escalates by label | Similar device to Zepbound; confirm coverage |
| Zepbound (tirzepatide) | Chronic weight management | Injection, weekly | Indication-specific steps to target dose | Mounjaro vs Zepbound differences center on labeling and access |
| Victoza (liraglutide) | Type 2 diabetes | Injection, daily | Gradual daily uptitration | Part of Saxenda Victoza family; earlier-generation GLP-1 |
| Saxenda (liraglutide) | Chronic weight management | Injection, daily | Stepwise daily increases | Lower average weight loss than newer weekly agents |
| Rybelsus (semaglutide) | Type 2 diabetes | Oral tablet | Fixed daily tablet with fasting rules | Rybelsus oral semaglutide suits those avoiding injections |
Bottom line on names and doses: match the indication, confirm the titration schedule GLP-1 plan, and verify whether semaglutide dosing or tirzepatide dosing aligns with your goals and insurance pathway.
Who Should—and Should Not—Use GLP-1s
Choosing a GLP-1 involves clear criteria and a realistic plan. GLP-1s are best for those with a high BMI and health risks. They work well with steady habits and regular doctor visits.
Clinical criteria: BMI thresholds and comorbid conditions
Wegovy and Zepbound are for those with a BMI of 30 or 27 with health issues like prediabetes. This rule helps doctors decide who can use these medicines. It also matches what insurance companies follow.
Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes first. They might be covered more if you have other health problems. But, not everyone loses a lot of weight, even with the right dose.
When GLP-1s are first-line vs. adjunct to lifestyle
GLP-1s are not a solo solution. They work best with healthy eating, exercise, and sleep. This approach is based on the idea that obesity is a chronic disease.
In some cases, doctors might start medication early. This is for people at high risk. Older adults might need extra protein and strength training to keep muscle.
Contraindications: pregnancy, breastfeeding, thyroid cancer/MEN history
Don’t use GLP-1s if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding. Also, avoid them if you have a family history of thyroid cancer or MEN. If you’ve had pancreatitis, talk to a specialist first.
Tirzepatide is not for people with severe stomach problems. If you have complex stomach issues or take many medicines, discuss the risks with your doctor.
Why “quick fix” or short-term cycles backfire with weight regain
Short-term use often fails because hunger and metabolism signals come back. Many people regain weight after stopping, which can be upsetting.
Long-term plans are better. They fit the chronic disease model of obesity. Goals, prevention of relapse, and follow-up help avoid cycling and support lasting results.
Safety, Side Effects, Compounded Products, and Insurance Realities
Patients must weigh the good against the bad when it comes to GLP-1 treatments. They need clear information on side effects, product quality, and how to get access. Doctors have to balance the benefits of treatment with the risks, while insurance companies decide who gets it and when.
Common side effects and everyday care often start in the gut. Symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation are common, mainly in the beginning. Doctors use a slow increase in dosage, smaller meals, and hydration to manage these issues.
They also recommend fiber and antiemetics for nausea. A slight increase in heart rate can happen; doctors watch heart rates closely and adjust doses if needed.
Labels for semaglutide and tirzepatide warn about delayed gastric emptying and rare severe GI events. Gallbladder issues and pancreatitis are rare but possible. If symptoms worsen, doctors stop treatment, check for complications, and then decide what to do next.
Protecting muscle while losing weight is crucial as doses increase. Losing weight too fast can lead to muscle loss, more so in older adults. Dietitians focus on getting enough protein and add supervised resistance training to protect strength and mobility.
Simple steps help: plan protein at each meal, lift two to three days a week, and keep a training log. These habits make it easier to maintain results when doses stabilize.
Compounded products demand caution. The FDA has warned about compounded semaglutide and tirzepatide that may include salt forms without safety or efficacy data. Reports of dosing errors and added ingredients highlight compounded semaglutide risks. Novo Nordisk states it does not supply semaglutide for compounding, and oversight for these pharmacies is not the same as for approved drugs.
Patients can confirm the exact active ingredient, request lot details, and discuss any adverse effects with their prescriber. When in doubt, clinicians favor FDA-approved brands with standardized dosing.
Insurance realities shape access. High list prices mean many patients face insurance prior authorization GLP-1 reviews. Plans often require documentation of BMI, weight-related conditions, and prior attempts at lifestyle changes. Some benefit designs mandate step therapy before covering newer agents.
Coverage for obesity drugs varies widely by employer and plan. Certain pharmacy benefit managers have shifted formularies, increasing denials or switches. Medicare GLP-1 policy limits coverage when the sole indication is weight loss, though coverage may apply for approved cardiovascular risk reduction uses.
To improve approval odds, clinicians submit clear records, note comorbidities, and prepare for appeals. Patients should ask HR about benefits, exclusions, and any pilot options that may widen access.
| Topic | What to Know | Practical Next Step |
|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 side effects | GI symptoms are common early; transient heart rate increases may occur; rare GI complications are documented on labels. | Use slow titration, hydration, fiber, and antiemetics as needed; report severe or persistent symptoms. |
| Muscle preservation | Rapid loss can cut lean mass, more so in older adults. | Aim for adequate daily protein and schedule resistance training two to three times per week. |
| Compounded semaglutide risks | Non–FDA approved products may include salt forms, variable dosing, and added ingredients. | Verify the exact active ingredient; prefer FDA-approved brands when possible; monitor for adverse events. |
| Insurance prior authorization GLP-1 | Plans may require documentation, step therapy, and evidence of comorbidities. | Submit complete records; ask about coverage for obesity drugs and exceptions. |
| Medicare GLP-1 policy | Limited for weight loss alone; some coverage exists for cardiovascular risk reduction indications. | Confirm the indication on the prescription and discuss Part D options with the plan. |
Between clinical care and coverage for obesity drugs, the path can be complex. With careful monitoring, smart nausea management GLP-1 strategies, and a plan for appeals, patients and clinicians can navigate step therapy and shifting formularies more effectively.
Conclusion
GLP-1 therapies have transformed how we treat obesity and diabetes. They show that, for the right people, these drugs can lead to significant weight loss. They also improve blood sugar levels and reduce heart disease risk.
Studies and real-world data show more benefits. These include lower rates of obesity-related cancers. But, we still need to study their long-term safety and how they work.
There are still myths to debunk. The difference between Ozempic and Wegovy is important. Ozempic is for diabetes, while Wegovy and Zepbound are for obesity. These drugs aren’t quick fixes. Stopping them often means weight gain.
The best results come from a treatment plan. This plan should include a doctor’s guidance, careful screening, and slow dose increases. It should also support healthy eating, exercise, sleep, and behavior changes.
Be wary of fake products sold as semaglutide or tirzepatide. Always choose FDA-approved brands from trusted pharmacies. Getting these drugs can be hard due to cost and insurance issues. But, discussions about these problems are ongoing.
Knowing the facts about GLP-1 helps everyone make better choices. In the right hands, these drugs are powerful for heart health. They’re not a magic solution, but they offer real benefits. With ongoing support, they can be a key part of modern care.
Sources for the articles:
- Wilding JPH et al. “Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity.” New England Journal of Medicine (2021).
- Rubino D et al. “Effect of Continued Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo on Weight Loss Maintenance.” JAMA (2021).
- Apovian CM et al. “Pharmacological management of obesity: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline.” JCEM (2015).
- Kushner RF & Kahan S. “Introduction: The State of Obesity in 2023.” Obesity Journal.
- U.S. FDA. “FDA-Approved Medications for Chronic Weight Management.”
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
Who should not take GLP-1s?
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
Who should not take GLP-1s?
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
What myths should I ignore?
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
Who should not take GLP-1s?
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
What myths should I ignore?
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
Who should not take GLP-1s?
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,349 per month, and Zepbound about
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near
FAQ
What are GLP-1 drugs, and how do Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound differ?
GLP-1 drugs mimic a hormone in the gut. They boost insulin and slow digestion. This helps control blood sugar and weight.
Ozempic and Wegovy both have semaglutide. But Wegovy is for weight loss, while Ozempic is for diabetes. Mounjaro and Zepbound also have semaglutide, but Mounjaro is for diabetes and Zepbound for obesity.
Are GLP-1s really “game changers” for weight loss and heart health?
Yes, they are. Studies show they help with weight loss and heart health. Wegovy users lost 15.2% of their body weight over two years.
Tirzepatide users without diabetes lost about 18% at the highest dose. They also cut major heart problems by about 20% in high-risk groups.
Is Ozempic FDA-approved for weight loss?
No. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes. Wegovy, with the same active ingredient, is approved for weight loss and heart health.
Mounjaro is for diabetes, and Zepbound is for obesity.
Why are GLP-1s suddenly everywhere—from celebrity buzz to social media?
They are visible and easy to use. People talk about them because of weight loss and how they work. This has made them popular.
Supply shortages and celebrity mentions have also increased interest. Insurers and PBMs have shaped how people can get them.
How do these medicines work in the brain and gut?
They work on brain areas that control hunger. This lowers the body’s weight set point. People often feel less hungry and full sooner.
In the gut, they slow digestion. This can cause nausea and other stomach problems, but these usually lessen over time.
What side effects should I expect, and how are they managed?
Common side effects are stomach problems like nausea and diarrhea. These often get better with time.
Small meals, staying hydrated, and fiber can help. Antiemetics can also reduce nausea. Rare risks include gallbladder disease and pancreatitis.
Do GLP-1s reduce cancer risk?
An analysis found a 17% lower cancer risk over eight years. This includes a 30% lower risk of ovarian cancer.
But, there was a small increase in kidney cancer. Experts say more studies are needed to be sure.
Who qualifies for Wegovy or Zepbound?
Adults with a BMI of 30 or higher qualify. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher and a weight-related condition also qualify.
For Ozempic and Mounjaro, you need a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Coverage may require documentation and prior authorization.
Are GLP-1s a quick fix for weight loss?
No. Obesity is a chronic disease. Stopping therapy often leads to weight regain.
Long-term management, including diet and exercise, is key. This helps keep weight off and protects health.
Who should not take GLP-1s?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take them. Those with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 should also avoid them.
Use caution if you have pancreatitis. Tirzepatide is not recommended for severe stomach disease. Always talk to a doctor first.
What about muscle loss during rapid weight loss?
Some muscle loss can happen, more in older adults. Eating enough protein and doing resistance training helps keep muscle.
Doctors may adjust the dose and monitor body composition. They can also tailor nutrition to protect muscle.
Are compounded semaglutide or tirzepatide products safe?
No, the FDA warns against them. Compounded versions lack safety and efficacy data. Dosing can be unpredictable, and side effects have been reported.
Stick with FDA-approved medications from trusted pharmacies. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply ingredients for compounding.
How much do these drugs cost, and will insurance cover them?
Prices are high. Wegovy costs around $1,349 per month, and Zepbound about $1,086. Ozempic and Mounjaro are often near $1,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.
,000 off-label.
Coverage varies by plan. Some may require prior authorization or step therapy. Manufacturer copay programs can help reduce costs for eligible patients.
What dosing schedules and half-lives should I know?
Semaglutide has a seven-day half-life, and tirzepatide about five days. Both are weekly injections with gradual dose escalation.
Rybelsus is the oral form of semaglutide for diabetes. But most obesity indications are injectable. Titration schedules vary by brand and indication.
Do GLP-1s help with conditions beyond weight and diabetes?
Yes, they help with heart health and other conditions. They reduce major heart problems and improve heart failure symptoms in certain groups.
They may also help with inflammation and addiction behaviors. Kidney outcomes and sleep apnea are being studied. They show promise for broader health benefits.
Why does a cardiologist’s perspective matter here?
Weight, insulin resistance, blood pressure, and heart health are closely linked. Cardiologists help assess risk and guide long-term management.
They ensure weight loss aligns with heart health. This is important as GLP-1 indications expand into cardiovascular prevention.
What myths should I ignore?
Myth: GLP-1s are brand-new. Fact: They’ve been used in diabetes care for over 15 years.
Myth: Ozempic is a weight-loss drug. Fact: Wegovy and Zepbound are approved for obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are for type 2 diabetes.












